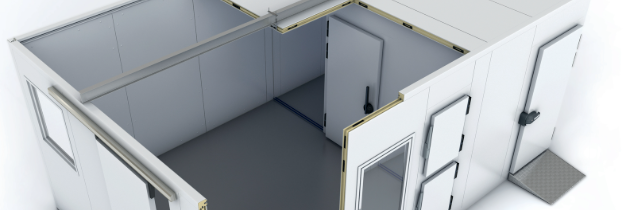
One of the most critical aspects of cold room construction is insulation. Polyurethane Foam (PUF) is commonly used due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal insulation properties, which collectively contribute to reduced energy costs. Another widely used material is polystyrene that offers higher compressive strength, whereas EPS is more cost-effective and performs well when combined with other materials.
The structural integrity and thermal performance of cold rooms are often ensured through insulated sandwich panels. These prefabricated panels have an insulating core—usually made from PUF or polystyrene—encased between metal or plastic sheets. For access, cold room doors are designed to be both accessible and airtight. Hinged and sliding doors equipped with sealing gaskets are preferred to minimize air leakage.
Refrigeration systems are another core component, encompassing compressors, evaporators, and condensers. Compressors must be energy-efficient and correctly sized to match the volume of the room. High-efficiency evaporators and condensers help maintain consistent temperatures with minimal energy use. Defrosting mechanisms such as electric, hot gas, or water defrost systems are necessary to prevent ice build-up, ensuring the refrigeration equipment operates smoothly.
Flooring also plays a significant role. It must be insulated to prevent thermal bridging and durable enough to handle heavy loads. Often, this involves using concrete with integrated insulation or specialized insulated floor panels. Vapour barriers are essential to prevent moisture ingress, which can lead to condensation and structural damage. Additionally, proper ventilation is crucial for managing air quality and humidity levels within the space. Together, these components help create a cold room that meets industry standards for energy efficiency and operational reliability.
Importance of Energy Efficiency in Cold Rooms
Energy efficiency is a fundamental aspect of cold room operation, directly affecting both operational costs and environmental impact. Cold rooms, particularly those in food storage, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology sectors, require consistent temperature control to preserve product quality. Energy-efficient systems are vital in reducing electricity consumption, which leads to substantial long-term savings. Lower energy use also means reduced greenhouse gas emissions, supporting sustainability goals and improving a company’s environmental credentials.
Meeting energy efficiency standards helps ensure regulatory compliance, which is critical in regions with strict energy usage laws. Efficient systems also offer greater operational reliability, minimizing the risk of temperature fluctuations that can compromise product safety. Additionally, using energy-efficient components reduces mechanical stress, extending the life span of the equipment and lowering maintenance costs. Consistent temperature control, made possible by efficient cold rooms, protects perishable items, reducing waste and enhancing consumer safety. Overall, prioritizing energy efficiency in cold room design and operation is an essential step towards sustainable and cost-effective business practices.
Materials for Constructing A Cold Room
Selecting the right materials is essential to the performance and longevity of a cold room. Thermal insulation is the most important consideration; materials with high R-values, such as polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene (EPS), are ideal as they minimize heat transfer and maintain a stable temperature. Durability and mechanical strength are also crucial. Galvanised or stainless steel panels are often used because they resist corrosion and wear, ensuring a long service life.
Moisture resistance is another key factor. Materials should incorporate vapour barriers—such as polyethylene sheets—to prevent condensation and mold growth, which can damage stored goods and the room itself. Hygiene is equally important, particularly in food and pharmaceutical environments. Smooth, non-porous surfaces that are easy to clean help meet strict sanitation standards.
Air tightness must be maintained to avoid energy losses. Construction materials should allow for airtight seals around doors, windows, and joints. EPDM rubber gaskets and silicone sealants are commonly used for this purpose. Fire safety is also a concern, and fire-resistant materials like rock wool and fibreglass are preferred for their protective properties.
Environmental considerations are becoming increasingly important in material selection. Sustainable and recyclable materials with low environmental footprints are favored, especially when they offer performance without compromising eco-friendliness. Cost-effectiveness is another essential factor. While high-performance materials such as polyurethane foam may have a higher initial cost, their superior insulation capabilities lead to significant long-term savings. Choosing materials that offer the best balance between performance, safety, and sustainability ensures a cold room that is both efficient and future-proof.
Cold Room Construction Panels for Walls and Ceilings
The choice of wall and ceiling panels significantly impacts a cold room’s energy performance and structural integrity. High-performance panels made from materials like polyurethane (PUR) and polyisocyanurate (PIR) are popular due to their excellent thermal insulation, durability, and ease of installation. PUR panels offer low thermal conductivity and are resistant to moisture and chemicals, making them ideal for humid environments. PIR panels go a step further with improved fire resistance and even better insulation, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces maintenance needs over time.
Using these high-performance panels results in several advantages. They maintain consistent internal temperatures, lowering energy use and operational costs. The panels also provide structural support, resisting external impacts and pressures. Their smooth, hygienic surfaces are easy to clean and inhibit bacterial growth, which is vital for maintaining sanitary storage conditions.
When selecting panels, several factors should be considered. Thermal conductivity is crucial; panels should provide high insulation performance to prevent temperature fluctuations. Fire resistance ensures compliance with safety codes, while moisture resistance protects against damage that can compromise insulation. Ease of installation is also important, as it reduces labor costs and construction time.
In conclusion, the use of high-performance panels in cold room construction is essential for achieving energy efficiency, structural reliability, and operational excellence. Choosing the appropriate panel type based on specific performance needs ensures a well-functioning, cost-effective, and durable cold room system.
If you would like to find out more information about constructing a modular coldroom you can contact us on info@coldsafe.co.uk. We can provide both the materials or fully install the modular coldroom for you.